Mental health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being. Yet many people go through life without fully understanding or addressing their emotional and psychological struggles. Whether someone is experiencing depression, anxiety, relationship issues, or a general sense of dissatisfaction with life, the root causes may not always be immediately clear.
This is where a full psychiatric evaluation comes in. In this article, we will explore the importance of a psychiatric evaluation. Read on.
What is a Full Psychiatric Evaluation?
A full psychiatric evaluation is a thorough assessment conducted by a psychiatrist or licensed mental health professional. This is to diagnose mental health conditions and understand the underlying:
- Psychological issues
- Emotional issues
- Behavioral issues
It has been used by many healthcare provider. This evaluation typically involves:
- A detailed interview
- Standardized assessments
- A review of the individual’s medical and family history
The goal of the psychiatric evaluation is to diagnose any existing mental health conditions. It also to uncover the deeper issues that may be influencing a person’s mental state.
The Components of a Full Psychiatric Evaluation
A psychiatric evaluation is a multifaceted process, and different professionals may use slightly different methods, but most evaluations share the following components:
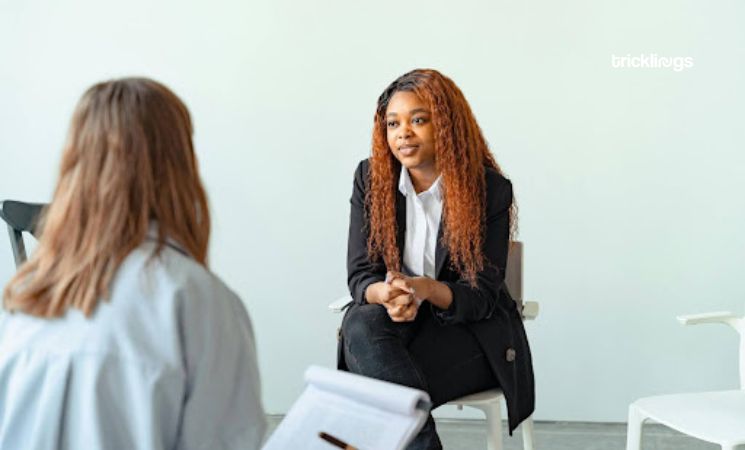
Clinical Interview
The clinical interview is the cornerstone of any psychiatric evaluation. It allows the mental health professional to gather detailed information about the individual’s current:
- Symptoms
- Emotional state
- History
- Lifestyle
Some of the key topics discussed during the interview include:
Presenting symptoms
What issues or challenges is the individual currently facing? This could involve:
- Mood swings
- Sleep problems
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Intrusive thoughts
Medical history
The psychiatrist will want to understand the person’s physical health and any previous medical treatments or diagnoses. This helps to rule out physical causes of mental health symptoms, such as:
- Hormone imbalances
- Neurological disorders
- Medication side effects
Psychiatric history
Has the person experienced any previous mental health issues or sought therapy in the past? This will help provide context for the current situation.
Family history
Mental health conditions can run in families. So understanding whether there is a genetic predisposition to certain disorders is crucial in diagnosing and identifying potential issues. Such as:
- Depression
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
Lifestyle factors
Some factors can significantly impact mental health, such as:
- Work
- Relationships
- Lifestyle choices
- Stress levels
Understanding these areas allows the evaluator to see the full picture of the individual’s life.
Psychological Testing
While a detailed clinical interview can provide a wealth of information, a psychiatric evaluation may also involve standardized psychological testing. These tests help assess the individual’s:
- Cognitive abilities
- Personality traits
- Emotional functioning
Some common types of tests include:
Personality assessments
These tests help identify personality traits, such as introversion or extroversion, and can shed light on underlying tendencies like:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Sociopathy
Tools such as the MMPI are widely used to assess personality disorders and other mental health conditions.
Cognitive testing
Cognitive tests assess a person’s thinking, memory, problem-solving abilities, and attention span. This can be helpful in detecting:
- Cognitive decline
- Learning disabilities
- Issues such as ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder)
Mood and anxiety assessments
Standardized questionnaires like the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) or the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) help quantify the severity of:
- Mood disturbances
- Anxiety
- Other emotional states
Observations and Behavioral Analysis
During the evaluation, the psychiatrist will also observe the individual’s behavior and body language. Subtle signs such as:
- Poor eye contact
- Agitation
- Disheveled appearance
- An overly flat affect may provide important clues
These observations can help identify potential issues that may not always be easily articulated by the patient. Such as:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Psychosis
- Other mental health conditions
Review of Medical and Family History
As mentioned earlier, understanding an individual’s medical background is essential for identifying possible physical causes of psychological symptoms. Many physical health problems, such as chronic illness, hormonal imbalances, or neurological disorders, can contribute to mental health symptoms. For example:
- Thyroid problems
- Neurological disorders
- Medication side effects
Similarly, a family history of mental health issues can reveal genetic predispositions to certain disorders. For instance, some conditions tend to run in families. Such as:
- Schizophrenia
- Bipolar disorder
- Major depression
So, understanding these dynamics can aid in a more accurate diagnosis.
How a Psychiatric Evaluation Identifies Underlying Issues
The real strength of a psychiatric evaluation lies in its ability to uncover the underlying factors contributing to a person’s mental health struggles. These underlying issues can vary significantly.
A thorough evaluation can help identify them so that appropriate treatment plans can be developed. This has been used in a behavioral health program. Here are a few examples of underlying issues that may be identified:
Unresolved Trauma or PTSD
Traumatic experiences, whether in childhood or adulthood, can have a long-lasting impact on mental health. Many individuals struggle with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) without fully understanding that their symptoms are linked to a traumatic event. During a psychiatric evaluation, a mental health professional can help individuals identify symptoms of PTSD, such as:
- Flashbacks
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Hypervigilance
This might have been triggered by past trauma. Often, PTSD is overlooked or misdiagnosed as a more general mood disorder or anxiety disorder. However, a full evaluation can bring these underlying experiences to light.
It allows for effective trauma-focused therapy to be implemented. Trauma might not always come from an obvious event like war or a violent assault. It can stem from:
- Childhood neglect
- Emotional abuse
- Even repeated stressful experiences over time
Identifying these patterns is essential for recovery.
Unrecognized Mood Disorders
Mood disorders such as depression or bipolar disorder are often misunderstood. A psychiatric evaluation can reveal if someone is suffering from a mood disorder that they may not have recognized. For example, someone may believe they are just experiencing “bad moods.”
However, a thorough evaluation might uncover underlying depressive or manic episodes that need medical attention. Bipolar disorder, in particular, is often misdiagnosed because its symptoms can be mistaken for other issues like:
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Even substance abuse
Understanding the nature of mood disorders is critical to finding the right treatment. A psychiatric evaluation may also help distinguish between major depressive disorder (MDD) and other mood-related disorders like dysthymia (persistent depressive disorder). This can lead to more effective and targeted therapy.
Anxiety and Stress Disorders
Chronic anxiety or stress can affect daily functioning. However, people may not always understand the extent of the problem. Through standardized tests and detailed interviews, a psychiatrist can determine whether someone has:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
They also identify specific triggers for anxiety. Often, anxiety disorders coexist with other conditions, such as depression, making diagnosis more complex. A full evaluation helps clarify the nature of these symptoms and whether they are part of:
- An underlying mental health disorder
- A result of external life stressors
The evaluation may help uncover physiological triggers of anxiety, such as:
- Adrenal fatigue
- Imbalances in neurotransmitters
This can contribute to feelings of constant tension and unease.
Personality Disorders
Some individuals may struggle with interpersonal relationships or extreme mood swings. This is without realizing that they have a personality disorder.
Personality disorders can deeply affect how someone relates to others. Such as:
- Borderline personality disorder (BPD)
- Narcissistic personality disorder
- Antisocial personality disorder
A psychiatric evaluation can help identify patterns of behavior and thought that may align with a particular personality disorder.
People with personality disorders might not always be aware of their behavior or how it affects their relationships. It makes this diagnosis essential. Recognizing the symptoms of personality disorders, such as chronic instability in:
- Relationships
- Self-image
- Emotions
This allows for targeted interventions and therapies that can improve social functioning and emotional regulation.
Attention and Focus Issues
Conditions like ADHD are often missed or misdiagnosed, especially in adults. A psychiatric evaluation can determine if an individual is experiencing:
- Attention deficits
- Impulsivity
- Difficulties with focus that align with ADHD
They also can suggest appropriate treatment strategies to improve functioning. ADHD isn’t just a childhood condition. It can persist into adulthood and impact:
- Academic performance
- Career success
- Personal relationships
Without a proper evaluation, people with ADHD might feel misunderstood or develop self-esteem issues. ADHD can coexist with other conditions like:
- Depression
- Anxiety
This makes it difficult to isolate the core issue. A thorough psychiatric evaluation can help tease apart these complex layers and develop a holistic treatment plan.
Co-occurring Disorders
Many individuals struggle with more than one mental health issue at a time. For example, someone may experience both anxiety and depression, or they may have a substance use disorder alongside a mood disorder.
A full psychiatric evaluation can help identify these co-occurring conditions. Also, guide treatment approaches that address all aspects of the individual’s mental health.
These overlapping conditions can complicate treatment. However, understanding all the contributing factors can lead to more effective, integrated therapy.
Get a Full Psychiatric Evaluation Now
In conclusion, a full psychiatric evaluation is a comprehensive and essential tool in identifying underlying issues that may be affecting an individual’s mental health. It provides a thorough understanding of one’s symptoms, behaviors, and personal history. This leads to a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
If you or a loved one are struggling, seek a full psychiatric evaluation to get the help and support you need. Schedule an appointment today!