Air quality is a crucial aspect of environmental health, closely linked to the overall well-being of populations. In urban centres such as Sydney, where industrial, vehicular, and population density contributes to air pollution, managing air quality becomes especially important. This article will delve into the importance of air quality monitoring in Sydney, exploring its benefits, challenges, and impact on public health.
Understanding Air Pollution in Sydney
Sydney, a vibrant metropolis, faces unique challenges related to air quality. Factors, including traffic congestion, industrial emissions, and even natural events such as bushfires, contribute to the city’s air pollution. Despite Australia’s vast landscapes and comparatively lower pollution levels than many other global cities, occurrences of poor air quality still present pressing concerns that necessitate continuous monitoring and regulation.
The Role of Air Quality Monitoring
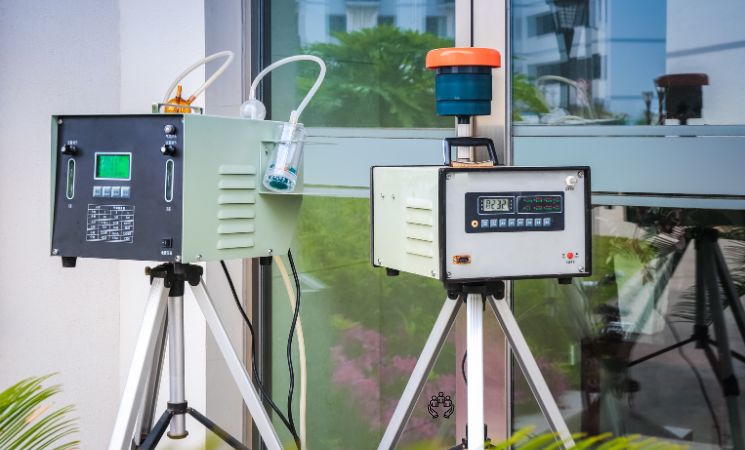
Air quality monitoring is a scientific method used to assess the level and types of pollutants in the atmosphere. Regular monitoring provides data that is essential for informing the public about the quality of the air they breathe and enables authorities to make evidence-based decisions to improve air quality and protect public health.
Data-Driven Strategies for Clean Air
Data collected through monitoring networks offer insights into pollution trends and help establish targeted strategies for improving air quality. This could include modifying industrial processes, revising traffic management, or initiating public health warnings during high-pollution events.
Health Implications of Air Pollution
Poor air quality has a direct correlation with respiratory diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and other serious health issues. Vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are especially at risk. Therefore, comprehensive air quality monitoring in Sydney can serve as a tool for minimising these health impacts and enhancing the quality of life for its residents.
Supporting Regulatory Compliance
Air quality regulations are in place to safeguard the environment and public health. Monitoring networks yield data that is crucial for ensuring that industries and other emission sources comply with these regulations. Timely and accurate monitoring can prompt corrective actions when air quality standards are breached, fostering a cleaner and safer environment.
Economic Benefits of Monitoring Air Quality
Investing in effective air quality management can have significant economic benefits. Reducing pollution levels leads to lower healthcare costs by decreasing the prevalence of pollution-related diseases. Moreover, a reputation for good air quality can enhance Sydney’s appeal as a tourist destination and place to do business.
Technologies in Air Quality Monitoring
Advancements in monitoring technologies have greatly improved the precision and convenience of air quality assessments. State-of-the-art equipment and methods such as remote sensing and real-time data analysis facilitate a more responsive and proactive approach to managing air pollution.
Public Awareness and Education
Awareness campaigns and educational programmes powered by reliable air quality data can empower individuals to make better-informed decisions about their activities. For example, on days of poor air quality, individuals may choose to limit outdoor exercise to minimise exposure to pollutants.
Challenges in Air Quality Management
Despite its critical importance, air quality monitoring faces several challenges. These can range from logistical issues, such as the placement of monitoring stations for optimal coverage, to the high costs of maintaining advanced monitoring equipment. Nonetheless, these challenges must be addressed to preserve the health of Sydneysiders and their environment.
Collaboration for a Cleaner Sydney
Effective air quality management is not solely the responsibility of governmental bodies — it calls for collective action. Communities, industries, and individuals must collaborate in a concerted effort to achieve and maintain clean air standards. Such partnerships can enhance compliance, drive innovation, and encourage sustainable practices within the city.
Conclusion
The air quality monitoring in Sydney plays a pivotal role in safeguarding the health of its residents and the environment. With the potential to deter negative health outcomes and stimulate economic growth, air quality management is an investment in the future of Sydney. By continuing to advance our monitoring capabilities, enforce regulations, and educate the public, Sydney can breathe easier and stride towards a healthier, more sustainable future.